Checking a cd or dvd. Utilities for resuscitation of damaged laser discs. Inf. about disk
Displays various information about installed CD/DVD drives, their characteristics, and the ability to read/write media of various types. In addition, VSO Inspector can scan disks for errors and check the readability of data written to them. Free. (gcontent)Download VSO Inspector (/gcontent)
Nero CD-DVD Speed
Version: 4.7.15
Size: 807 Kb
Status: free
(gcontent)Download Nero CD-DVD Speed (/gcontent)
A free utility that is part of the paid Nero. More than one generation of testers have been convinced of the indisputable results of the benchmark test for checking the quality of an optical drive.
The program can test how well the drive copes with reading and writing disks of various types, how much time it spends searching for blocks of information, how fast it can transfer data, how much it loads the central processor, how much it takes to spin up and stop the disk, is everything in order with the interface .
There is also additional information, but they are of less interest. The report on the work done is presented in the form of a visual graph, on which problem areas are immediately evident. In addition, the utility is able to check the quality of the discs themselves at the same time and try to collect basic information about them. Support for Blu-ray and HD DVD has been added and optimized in recent versions, but this will not be as relevant in the coming months. You may have a legitimate question, why do you actually need to test your drive? I will answer.
For example, it is far from uncommon when a drive ideally records discs of only one type (for example, everything is in order with DVD + R, but DVD-R - through a stump deck). Having found out this not the most pleasant fact, you can choose the type of media that suits you.
Windows system maintenance.
Any, even the most good and reliable thing needs care. The computer is no exception to this rule. With regular and frequent use, the computer sometimes accumulates some system "garbage", which is useful to periodically clear and eliminate. You may not immediately feel that there are problems, but if it becomes noticeable that the computer is running slower, and at the same time there is not enough space on the hard drive, some files refuse to load, and programs refuse to work, then it's time to start cleaning.
Most of these problems can be avoided, and the influence of others can be noticeably weakened, if you regularly engage in preventive and "cleansing" activities. Moreover, if some errors occur, the stability of the system may be compromised, which can lead to the accumulation of errors, and as a result, important files may be corrupted.
Check disk
Information on a hard drive is stored in a rather complex way, although this provides both quick access to information and the ability to easily access free space for creating new files.
In short, information about the storage location of files is concentrated in a special area of the disk. The way this information is represented and accessed is called a file system. IN WindowsXP different file systems are used: systems based on file allocation tables(FAT16 AndFAT32) or system NTFS.
Every time a file needs to be opened, such as when a program is started, the operating system consults the file system tables to find out where your data is actually stored on the disk.
Such a system is only good if it works perfectly. Indeed, if somehow the correspondence between what is written in the table and what is actually on the disk is violated, the consequences of this can be unpredictable: access to the necessary information may not be possible.
Could this happen? Unfortunately yes. Although the operating system itself usually handles the hard drive quite neatly and correctly, the same cannot be guaranteed with respect to any other program, especially when difficult situations arise. In particular, there is a high probability of errors occurring when the computer shuts down incorrectly (for example, as a result of a sudden power outage), when the system “freezes” for some reason, when the connection is interrupted unexpectedly during data transfer via the modem, when trying to set an unacceptable for the controller disk frequency of the main bus of the motherboard during the "overclocking" of the processor.
In this case, a number of problems specific to each particular file system may arise. The annoying thing about these problems is that you may not find them until it's too late. It is possible that these errors will manifest themselves in the form of a reduction in the size of the hard disk, partial corruption of information in files, and other unpleasant effects with an unobvious cause. In general, it is much better if there are no problems.
Detect problems and prevent future troubles in advance possible by performing regular checks. IN Windows XP The mechanism for performing such a check is very simple. Open the window My computer and select the drive you want to check. Click on its icon right click and select the item from the context menu that opens. Properties. On the tab Service press the button Run a check on the panel Disk check.
A dialog box will open Check disk options. It is recommended to check the box Automatically
fix system errors. If set and checkbox Scan and repair bad sectors, the program will check the physical state of the disk surface.
Before starting a disk check, it is recommended to close all running programs in order to exclude the possibility of accidental access to the disk. But even in this case, the operating system may consider some of the disks busy. In this case, you will see a message prompting you to perform a disk check after the system reboots. If you accept this offer, Check Disk will be performed during the restart of the computer.
How often should you check the disk health?
Weekly checks are more than enough. If you regularly find that there are no problems, then you can check even less often. But if some unpleasant event occurred: incorrect shutdown Windows a power surge, a “freeze” of the machine, then after a reboot, immediately check it, suppressing future problems “in the bud”.
Disk Checker
Disk Checker is a utility for checking media for bad spots and fixing any errors found. Listed program features:
· checking the entire surface of the disk using low-level access,
· file check,
· S.M.A.R.T information output. for hard drives
· checking floppy disks and CD / DVD, as well as network and RAM disks.
The utility can be used as a backup tool, since it is able to create disk images compatible in format with such well-known packages as Diskcopy, WinImage, DiskDupe, including burning CD-ROM/DVD .ISO files. It is possible to format disks. The program supports command line parameters and integrates into the Windows context menu for quick launch of checks.
In computer technology, any information is represented in the form of a numerical code, which is called binary. The smallest unit of information representation - bit. Information is processed in groups of 8 bits - bytes.
Bytes are encoded and text, and music, and drawing. A computer must be able to distinguish one kind of information from another. To do this, a special header is placed before a group of bytes, which explains what these bytes stand for. And in order for the computer to determine where the header bytes end and the data bytes begin, the header and data must have a well-defined format. Different types of information use different formats. For example, if this is a black and white picture, then each byte after the header determines the brightness of each next point, and if it is a color picture, then the color of one point can determine not one byte, but several bytes.
Neither a bit nor a byte can be stored as information, since it is not clear what they mean (letters, notes, colors, etc.). You can save any sequence of bytes by adding a header (name) to it. After registering in the computer, this sequence of bytes will be called file.
File is the smallest unit of information storage containing a sequence of bytes and having a unique name. By the name of the file, the computer determines where the file is located, what information it contains, in what format it is written, what programs it can be processed.
Data in the form of files is stored on magnetic disks - hard or floppy. Each file on the disk has its own address. When a file is opened, the drive head moves to the desired location on the disk and reads the specified file into RAM. To unambiguously determine the location of any file, disks must have a clear physical and logical structure. This structure is created in the process formatting disk.
Formatting is divided into low-level formatting (physical) and high-level formatting (logical).
Low-level formatting breaks the disk into tracks- concentric circles, numbered from the edge to the center. The outer track (zero) contains service information.
To increase the amount of stored information, hard disks consist of several magnetic disks, the surfaces of which are serviced by separate heads. But conventionally they consider that this is still one disk, which has not 2 sides, but 8 or 16. Each of these disks is also divided into tracks. Tracks with the same number are called cylinder. Information is written to the disk along the cylinders - from the edge (zero) to the center.
The tracks, in turn, are divided into sectors. A sector is the smallest unit of information that can be written to or read from a disk. At the beginning of each sector there is a service area, followed by a data field and a control code field. The heading indicates the number of the cylinder, head and sector itself. It may also contain a note about the defective sector, which serves as an indication of the impossibility of using it for data storage. The reliability of these indications is checked using a control code. Sector headers are written during the low-level format operation for the entire track at once. The standard size of the sector data field is 512 bytes.
When formatting the top level, the following actions are performed:
1. The data area is marked using an electromagnetic field created by the recording head of the drive. The markup is used to write and read information, correct the speed of rotation of the drive. The disk data area is divided into clusters– groups of adjacent sectors. A cluster is the minimum size of an addressable space. Each cluster has its own number. The cluster size (number of sectors) is selected as a multiple of the power of 2, depending on the volume of the disk and the size FAT. A file on the disk is allocated an integer number of sectors, but not less than one. If a file occupies more than one cluster, then all clusters occupied by the file are organized into chain of clusters.
2. The boot sector is written. It contains a table describing all disk parameters, as well as a short program used in the OS boot procedure. If the disk is being prepared as a system disk, then there will be an OS boot program. If not, there will be a program that, when trying to boot from this OS disk, will display a message that this disk is not a system disk.
3. Recorded FAT- a file allocation table in which the computer remembers the addresses of recorded files. If you need to read a file, then the computer finds its address in this table by its name and transfers the magnetic head of the drive to the right place to read it. If the file allocation table is corrupted, the information on the disk will be lost. Physically, of course, it will remain there, but it will not be possible to address it. That's why FAT duplicated for reliability. In case of any damage, the computer itself restores this table from a copy. Thanks to this, you can work with a computer for years and not lose information. MS DOS and Windows use file systems FAT16 And FAT32. File address in FAT16 written as a two-byte number (16 bits), i.e. there are 2 16 different addresses in total. This means that the maximum number of files on a disk is 65536. Modern hard disks have very large volumes, and they do not have enough addresses. If the disk size is, for example, 2 GB, then the cluster size will be 32 KB (2GB/65536). This is much larger than the sector size (512 bytes). No matter how small the file is, it will still take up a whole cluster, and all unused sectors in it will simply disappear. IN FAT32 the address is written as a four-byte number. It is clear that in this case there are more addresses, and the cluster sizes are smaller. Irrational losses are reduced.
Video editors, converters, DVD burning.
Program Overview
Programs for testing CD/DVD/Blu-Ray discs (part 1)
When we hear the phrase "counterfeit products", the first associations are with DVDs and movies. Unfortunately, when buying a DVD disc, we can almost never guarantee its quality. In this regard, the question arises of testing this disc. There are many paid, for example, Nero, and free utilities for checking the quality of DVD discs. One of them - VSO Inspector Vso-Software allows you to determine the characteristics of a CD/DVD/Blu-Ray drive, obtain information about the inserted disc (both blank and recorded), and perform surface analysis for read errors.
Free program VSO Inspector fully Russified, has a volume of about 3 MB, works with all operating systems Windows before 7 inclusive. You can download the latest version of the program from the download page of the developer's website by clicking on the link Download Latest Version.
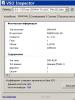
Program installation VSO Inspector runs as usual, and before completion you will be asked to familiarize yourself with the main features of testing disks. The main window of the program is shown in Figure 1:
Fig.1. The main window of the disk test program VSO Inspector
Bookmark Device the main parameters of the disk drive (disk drive) are displayed: general information, options, the ability to read and write various disks, etc. (Fig. 1).
Next bookmark, Carrier, will provide information about the CD / DVD / Blu-ray disc (blank) inserted into the drive: media type, manufacturer, number of layers, maximum read / write speed, etc. - Fig. 2:

Fig.2. Disk parameters tab (blanks)
Bookmark Scanning you can check the quality of the discs: perform a surface scan and test the files if the disc contains recordings. The testing process is reflected in the diagram and numbers in the corresponding colored cells: Good, Bad and Errors. To select a test, check the box next to the desired item and click the button Start. In the presence of errors and bad sectors, testing the disk surface can take a long time - see Figure 3.

Fig.3.
At the end of the scan, a summary of the test results is displayed, which can be saved as a file - button Save. Unlike similar programs, VSO Inspector allows you to check not only the quality of the surface, but also errors in the information already recorded on the disk - point File testing. In addition, you can view detailed information on each sector of the disk - tab View sectors(Fig. 4).

Fig.4."View disk sectors" tab
Thus the program VSO Inspector- a good tool for testing disks. It should be borne in mind that the presence of errors on a rewritable CD / DVD does not mean that they should be thrown away. Sometimes after performing a full (not quick) erase, for example, using a program Nero, the errors disappear and the disc can be used again.
Introduction It is extremely rare these days to find a computer without an optical drive. CD-ROM, CD-RW and DVD-ROM drives have firmly entered our lives. It's almost impossible to get by without them. The volume of software packages has long been many times greater than the capacity of a standard 3.5" floppy disk, not to mention the extremely low speed of 3.5" disk drives. A few years ago, devices appeared on the market that allowed recording on DVD and, at the same time, on more familiar CD-R and CD-RW media. In principle, the technical characteristics of any representative of the optical storage class can be read in the documentation or found on the manufacturer's Internet sites. It seems that everything is simple. I looked at a model with the required speed and a list of desired features, then bought it and enjoy life. This is where you can come across “nuances” that can ruin your mood. As the well-known folk wisdom says - “It was smooth on paper, but they forgot about the ravines.” The problem is that not all drives in real work behave the way they are expected to.
Many drives can show in practice the data reading speed significantly different from that declared by the manufacturer. Not all of them work equally well on all types of media, not to mention situations where they have to deal with damaged disks. Copying audio CDs and burning them, when you want to get a perfect copy, completely identical to the original, is not possible for all drives. In addition, most manufacturers do not indicate a number of specific features of the drives, which in some cases can play a decisive role in the manufacture of exact duplicate discs.
Finding out how good or bad this or that optical drive really is is possible only during testing. Programs that allow you to do this can be divided into two groups. The first includes specialized utilities specially designed for testing optical drives. The second group includes programs designed to work with drives, whose functions can be used to evaluate the operation of devices in practice.
Specialized programs
The most popular among specialized utilities designed for testing drives on optical media is the product package under the Nero brand. Their advantage is a set of wide features, combined with free and small volume, which allows them to be downloaded without problems from the site www.cdspeed2000.com. In addition to them, there are a number of special programs that can also be used for these purposes - they will be discussed below. One of the best programs for testing CD-ROM, CD-RW and DVD-ROM drives today is Nero CD Speed. In addition to the performance characteristics of drives, it allows you to obtain data on a number of their additional features.The set of basic (basic) tests consists of:
Transfer Rate (speed of reading data from the media)
DAE Quality (quality of extracting audio tracks)
Seek/Access Times (seek/access time)
CPU Usage (CPU usage)
Burst Rate (data transfer rate to the drive)
Spin Up/Down Times (disc acceleration/deceleration time)
Load/Eject Times (tray load/eject time)
Let's take a look at each of these tests in turn.
Transfer Rate Test allows you to measure the speed of reading data from the surface of the media. During the test, the program builds a graph that displays two lines. One of them, green, shows the data transfer rate. The second, yellow, shows the spindle speed. The resulting graphs are a reflection of the technology used in the tested drive. The horizontal data rate line indicates the use of the CLV (Constant Linear Velocity) method - constant linear speed. The straight line on the graph, going upwards, indicates the use of CAV (Constant Angular Velocity) technology - constant angular velocity. Most modern CD-ROM drives are based on this method. The graph with the transfer line going first obliquely upwards and then horizontally reflects the use of P-CAV (Partial-CAV) technology. Finally, the final image from individual horizontal sections indicates the Z-CLV (zoned-CLV) method used in the storage ring.
In order to fully reveal the speed potential of the carrier, it is necessary to take a disk with a volume approaching the maximum value for testing. The media must be of high quality and not have any scratches or other artifacts on the working surface.
DAE Quality Test- shows how well the drive is able to extract audio tracks. The first few audio sectors are written to the hard drive. The same sectors are then read again and compared with what was written to the hard drive. Depending on the presence of discrepancies, a score is set from 0 to 10. The last value indicates the ideal quality.
Seek/Access Times- This test determines the search or access time in three categories. Random - addressing the drive to randomly selected places on the disk. 1/3 - the drive moves one third of the length of the disk, starting from the beginning. Full - circulation occurs along the entire length of the disk from its beginning to end.
The user can choose which time will be determined during the test: Seek or Access. The difference lies in the fact that in the latter case, not only the beam is moved to the required position, but one sector is also read. This takes a few extra milliseconds.
CPU Usage Test- allows you to determine how much a particular drive consumes CPU resources during its operation. Measurements are taken at 1X, 2X, 4X and 8X speeds. The result is given as a percentage.
Burst Rate Test determines the data transfer rate to the drive. The result is correct only if the drive caches the data. It is not recommended to use this test with audio CDs.
Spin Up/Down Times- this test allows you to determine one of the dynamic characteristics of the drives associated with their ability to spin up and stop the disks. The less time these steps take, the better the drive performs. Spin Down measures the time it takes for the media to stop, while Spin Up measures the amount of time it takes for the drive to read data.
Load/Eject Times- during this test, in addition to the time required for the extension and cleaning of the tray, another indicator is determined. It is the time required to recognize the disc. The smaller it is, the faster you can start real work with a new carrier.
In addition to a set of standard tests, Nero CD Speed has a set of advanced features that can be successfully used for more detailed tests. Among them, first of all, we can note the possibility of recording a special test disc (CD-R or CD-RW). It provides in-depth testing of drives' ability to correctly extract audio tracks from digital audio discs.

Advanced Quality DAE Test just allows you to identify the slightest errors when testing this special disk.
data errors- indicates the number of incorrectly read audio samples. They are usually caused by poor media quality. In order to get rid of errors of this kind, you need to use high-quality disks or reduce the speed of the drive. If the number of errors is not too high, then the drives are usually able to correct them using the internal correction procedure.
Sync Errors- timing errors occur when the drive is not able to read the audio sector requested by the application, but extracts information from the neighboring one. As a result, some samples are lost or duplicated.
The maximum quality score for extracting audio tracks can be 100. It is based on measuring the number of errors during testing. The latter is carried out in two categories. The sequential read test emulates the drive under ideal conditions, which most models pass without problems. The second harmonic reading test is more difficult for drives, and this is where many of them make mistakes.
After checking the drives for DAE-quality, the program determines their ability to create copies of an audio disc on the fly in the 1X-16X speed range.
In addition to checking devices for the quality of extracting audio tracks, the test also checks the advanced capabilities of drives.
offset- all drives start reading audio sectors not from the real starting position, but from a place slightly different from it. This offset is usually less than 100 samples. Writers are also unable to start recording exactly from the starting position. As a result of the test, the value of the offset when reading or writing is given.
Read Leadin- the indicator indicates the ability of the drive to read information before the start of the starting position from the introductory zone. This is necessary to obtain exact copies of discs.
Read Leadout- a positive result indicates that the drive can extract information from the output zone going at the very end of the disk, after the working area. This makes it possible to obtain absolutely identical copies.
CD Text- indicates the drive's ability to extract CD Text information.
Read Subchannel Data- indicator indicates the drive's ability to read data from Subchannel. The latter contains information about index markers, number of tracks, etc. In the case of a positive result, it is possible to obtain perfect copies.
Another interesting feature of the Nero program is the use of the Overburning Test in the case of burners. What is it and what is it for?
The vast majority of modern writing drives can operate in Overburning mode. By this is meant the possibility of recording on media an amount of information that exceeds their official capacity. This quality of drives can be very valuable in certain situations. For example, when you start writing something to a disk, and several megabytes of data do not fit on it, forcing you to use additional media. Using the Overburning mode can very often solve this problem and save you money and time.
The very possibility of recording an additional amount of information is obtained due to the fact that all modern drives are able to work with CD-DA. All digital audio CDs are produced in accordance with the Red Book standard. Its requirements include that after the program area, which allows you to place up to 99 tracks, there is a Lead Out - a digital silence zone consisting of empty sectors. This gives at least 90 seconds of time. It is this section that can be used to record an additional amount of information.
Overburning Test allows you to determine the fundamental ability of drives to work in the mode of recording an additional amount of information and determine how much of it can be written to a particular medium. The maximum amount of data that can be written to it depends on the drive itself and on the properties of the disk itself.

During the test, media is inserted into the burner and the write speed is selected with the maximum capacity. During the test, nothing is physically written to the disk. If the test is successfully completed, information about the maximum possible amount of recorded information for this medium and the amount of data that can be recorded beyond the official capacity appears on the screen. In practice, these values will be slightly smaller due to the fact that when writing during the test to the last position, the drive still stores data in the buffer.
We have described the main features of the Nero CD Speed program directly related to testing drives. In fact, they are somewhat wider. Among these features there are a number of additional, quite useful in some cases. For example, the ability to create a Data CD, where the files will completely occupy the entire capacity of the disk. It can be used later to check the speed of reading data. In addition, when testing recorders, it can also be used to determine the write speed.

The program is basically similar in its main features to another Nero utility - CD Speed. The difference lies in the fact that it is designed specifically for testing drives specifically when working with DVD. When using DVD drives with other media, you can use Nero CD Speed. The list of basic tests of the DVD Speed program is as follows:
Transfer Rate
Access/Seek Times
CPU Usage
Burst Rate
Spin Up/Down Times
Load/Eject Times
layer change
Only the last of them needs explanation. It determines the time required to refocus the laser from one layer to another. The meaning of all other tests is the same as those described in Nero CD Speed.


Using the CD-DAE program, you can evaluate the quality of the drive's work on extracting audio tracks and converting them to Wav-files on your hard drive. For this, a digital audio disc is taken, all tracks are marked on it for greater reliability, and the Start button is pressed. In the process of extracting tracks and creating sound files on the hard drive, the program checks their contents, and if errors are found on the acoustic phonogram, the color changes from green to red. The total time spent on this procedure and the operating speed of the drive are a reflection of the drive's performance in such operations. The number of errors that occurred when extracting audio tracks reflects the quality characteristics of the drive. CPU utilization can be valuable information when multiple tasks are running on the computer at the same time.
CDVD Benchmark
One of the universal programs that allows you to test drives with CD and DVD media is the CDVD Benchmark program (www.cd-bremse.de). Its main advantages are efficiency, information content and the issuance of only the most important resulting information. In addition, the program provides the possibility of using special reference disks. The only inconvenience for most English-speaking users may be only the German interface. The small size of the program allows you to easily download it via the Internet and use it at home.The first item on the Datei main menu gives access to general commands. Of these, Laufwerkinfo generieren is of the greatest practical interest, allowing you to obtain information about the system, including the optical drive used.
The second item of the main menu allows you to run all possible Alle Tests Starten tests in a row, or select only one of them. Even lower, the Fehlerkorrektur-Test option allows you to build a graph of the speed of reading from the surface of the media, including from the reference disks of the ABEX line, which are not sold in Russia. The last Einstellungen item of this menu subgroup allows you to refine the operating parameters of this procedure to your liking before testing.
When you click on the third item Ansicht of the main menu, you get the opportunity to refine the final appearance of the final chart. We are talking about the absence or presence of any characteristic lines or conditional symbols.
The fourth Fenster item of the main menu allows you to set the size of the graph area on the screen, thus adjusting it in the best way for your monitor.
Finally, the last Hilfe option on the top menu traditionally provides help to the user. In this version of the program, this is interpreted as collecting system information and obtaining information about the version of the utility.
Now let's look at the final screenshot obtained as a result of testing the drive with an audio CD. The screen is divided into two halves. In the left of them, the green line shows the speed of rotation of the spindle, the white line shows the speed of reading from the surface of the disk. The red horizontal line shows the average reading speed. On the right half of the screen, the values of random search, random access and random access along the entire length of the string, obtained during testing, are given by conditional icons of different colors. The red horizontal lines show the average values of these parameters. At the very bottom of the screenshot, on two horizontal bars from left to right, the program gives the average reading speed in "X" and then the minimum and maximum values, then these three values are given in Kb / s. Following them is the operating range of read speeds of the drive on the tested media (as it is positioned by the program itself). Under the familiar word CPU is the CPU load at the 1X speed selected before the start of the test. Next come the self-explanatory values of the average search, access, and access times over the entire length of the string. Then comes confirmation of the ability of the drive to work with "exact flow" and C2 errors. The last characteristic expresses the data transfer rate on the interface.
Exact Audio Copy (EAC)
The EAC program, designed to extract audio tracks, can be successfully used to test drives with optical media. Naturally, we are talking about studying the characteristics of drives when working with audio discs.

Of course, this program can be used by analogy with the Nero DAE utility to determine the total time for extracting audio tracks and the number of errors made during this procedure. But apart from this, the EAC program has another interesting feature.
We are talking about the ability of the program in the "Drive Options" option to determine whether the drives support three important hardware characteristics, which can later be used to fine-tune the audio track extraction mode. In this case, we are talking about such properties of the drive as the ability to work with C2 errors, support for the Precise Stream function, and data caching. The presence of the first two is highly desirable for obtaining accurate audio copies. Support for caching, on the contrary, can interfere with this goal.
EAC version 0.95 Beta 3, available at the time of this writing, is very small - 1.24 MB and available for free download. The word Beta in its name should not cause confusion. The utility works quite reliably and is permanently in the process of fine-tuning.

It would probably be wrong on our part if, among the programs released under the Nero brand, we do not mention one more. It's about the Info Tool. Strictly speaking, it is not a test - it is a diagnostic utility. The information it extracts from the drives is in some cases very useful. In particular, the Info tool allows you to get information about the firmware version (firmware), buffer size, hardware-supported read and write capabilities, and operating modes. For DVD drives, you can find out if (RPC2) or not (RPC1) the region lock code is present.
CDROM Drive Analyzer

Using the CDROM Drive Analyzer utility, you can analyze the speed of reading data from the disk surface by the drive. The results are displayed in the form of a graph. It also reflects the values of the maximum and minimum speed, as well as the number of errors in the read blocks.

One of the many features of the Sandra Professional program is the ability to evaluate the performance of drives - CD-ROM/DVD Benchmark. The resulting performance index is calculated based on the read test (buffer/random/sequential) and the seek time test. Using CD-ROM/DVD Benchmark, you can evaluate the performance of drives when working with media of two categories Data CD or VideoCD/DVD.
General purpose programs
In addition to special programs for testing drives on optical media, you can use programs that can be used to record and copy discs. There are quite a lot of them, but we will focus only on the two most popular of them.
The CloneCD utility is very often used by users due to its ability to create exact duplicates of copied discs, including protected ones. With its help, you can control the real time required by the drive to copy a disc or record its “double”. The program can also serve as a criterion for evaluating the drive's ability to work with protected disks.

Ahead Nero Burning Rom
One of the most popular and widespread programs for burning to optical media is Ahead Nero Burning Rom. It can be used to control the actual speed of work with different categories of media.Conclusion
The most objective picture of the real capabilities of optical drives can only be given by a comprehensive set of tests. It should include appropriate specialized programs and a set of actions that simulate work in practice with specific most common applications. Each drive must be tested to work with all possible media types. To check the ability of drives to read information from damaged media (you can prepare a special disk that recreates a similar situation).After burning a CD, if you want to install drivers, programs or an operating system from it, you must definitely check it!
How to do it?
1st stage.
Free download of CDShot CD checksum calculator (1.6 MB). Installation is not required.
If you have x64-bit OS, then download: CDShot_x64.
We put the CD in the optical drive, - run the downloaded file sdshot.exe.
Picture 1
Select the drive with our CD and press the button hash.

Figure 2
If the message “Error: 32. The process cannot access the file because this file is occupied by another process” appears, close the message by pressing the button OK. We are looking for a process. … You will most likely have to close the My Computer window. And press the button again hash.

Figure 3
We are waiting for the end of the calculation of hashes ...

Figure 4
Let's see the result.
If the CS (CRC32, MD5 and SHA-1) match those specified in the description, then everything is fine! Press the button OK, - then Exit.
If you don't have checksums, then we compare them with the checksums of the image from which you burned this CD. We look:
If everything is fine with the checksums, then you can proceed to the second stage, - Scanning the disk (Surface test).
2nd stage.
Download utility Nero CD-DVD Speed v4.7.7.16. Installation is not required. Run the file CDSpeed.exe.

Figure 5
Select the drive with our disk, open the tab Disk scan, set the speed Maximum and press the button Start.
At the end of the test, the presence of yellow or red sectors indicates poor-quality "burning"! It does not make sense to install anything from such a disk, since errors are possible during the installation process. Using the bottom field engine, you can view damaged (poorly readable files).
If all sectors are green, the disc has been written without errors and is ready for use.